Which method do you find preferable for e-waste disposal?
 16 Oct, 2023
16 Oct, 2023 
The term “e-waste” refers to wastes produced by outdated electronics and home appliances meant for recovery, recycling, or disposal because they are no longer suitable for serving their original purpose. These wastes cover a wide range of electrical and electronic devices, including big home appliances like refrigerators and air conditioners, as well as handheld cell phones, personal stereos, and computers. Over a thousand different substances can be found in e-waste, many of which are toxic and may be dangerous to both human health and the environment if improperly managed.
In order to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals and minimize the negative effects of E-waste, proper E-waste management and monitoring are crucial.
Sources of E-Waste
- E-waste is generated from the products used for data processing, such as computers and computer devices like monitors, speakers, printers, keyboards, etc.
- Electronic devices that are used for entertainment like DVDs, TV, and CD players.
- Equipment or devices used for communication like landline phones, mobile phones, faxes, etc.
- Household equipment like vacuum cleaners, microwave ovens, washing machines, air conditioners, etc.
- Audio and visual components such as VCRs, Stereo equipment, etc.
Effect of E-waste on Human Health
Electronic technologies that have developed over the course of human history have helped and enhanced how we live, work, and play. But along with technology’s advantages comes its share of health risks from electronic waste. Electronic waste, or “e-waste,” has been known to cause environmental harm for some time, but most people are unaware of how hazardous it is to your health.
When e-waste undergoes dismantling, shredding, acid baths, and incineration processes, there is a chance of mishaps like cuts and burns. Heavy metals like lead, which affect the nervous system, blood, reproductive system, kidneys, and the development of children’s brains, can have permanent effects. Some of the known health issues brought on by exposure to e-waste include miscarriages, changes in thyroid function and development, decreased lung function, and mental health problems (such as changes in temperament and behavior). Other reported negative effects on health are genotoxicity, abnormal thyroid function, fetal loss, prematurity, low birth weight, and congenital malformations.
E-waste Disposal Methods
E-waste contains both hazardous and non-hazardous substances in their components. These hazardous substances, like plastic, lead, mercury, cadmium, arsenic, etc., pose health hazards to human beings the most when treated in uncontrolled conditions via air, water, and soil. Thus, E-waste disposal is an important aspect. Some of the e-waste disposal methods are-
Recycling, Reuse, and Recovery Options
The composition of e-waste consists of diverse items like ferrous and nonferrous metals, glass, plastic, electronic components, and other items, and it is also revealed that e-waste consists of hazardous elements. Therefore, reducing the concentration of these hazardous chemicals and elements through recycling and recovery is the main strategy for treating e-waste. In the process of recycling or recovery, certain e-waste fractions act as secondary raw materials for the recovery of valuable items. The following unit operations are a part of recycling and recovery.
- Dismantling- Removing parts with hazardous materials Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), Hg switches, Printed Circuit Board (PCB); removing parts with valuable materials that are simple to access (cable with copper, steel, or iron; parts with precious metals, such as contacts).
- Segregation of ferrous metal, non-ferrous metal, and plastic – This separation is normally done in a shredder process.
- Refurbishment and reuse – Used electrical and electronic equipment that can be quickly repaired and put back to use has the potential to be recycled and refurbished.
- Recycling/recovery of valuable materials – Ferrous metals in electrical furnaces, non-ferrous metals in smelting plants, and precious metals in separating works.
- Treatment/disposal of dangerous materials and waste – Shredder light fraction is disposed of in landfill sites or sometimes incinerated (expensive), Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are treated thermally, Printed circuit boards PCB is incinerated or disposed of in underground storages, Mercury is often recycled or disposed of in underground landfill sites.
Incineration
The benefit of e-waste disposal through incineration is the reduction of waste volume and the use of combustible materials’ energy content. For recycling, some plants remove the iron from the slag. Some organic materials that are harmful to the environment are changed into less harmful compounds through incineration.
However, there are certain disadvantages of e-waste disposal by the process of incineration as well. They are-
- The high cost of the infrastructure and equipment required to construct an incineration plant is a major factor in the cost of installing a waste incineration facility.
- Acid gases, including but not limited to the carcinogen dioxin, particulates, heavy metals, and nitrogen oxide, may be present in the smoke produced during the burning process. The environment is poisoned by these gases.
- In areas where incinerator plants are built, respiratory issues, elevated cancer rates, abnormal reproduction, and other health effects are frequent. The leftover ash needs additional treatment because it is filled with heavy metals and several poisons. It can seriously harm the public and the environment if improperly disposed of.
- Recycling and waste reduction are not encouraged by incinerating waste. No society would deliberately pursue this course of action. Reduce waste as much as possible and recycle it as much as possible.
Landfilling
This method of e-waste disposal is the most popular. Soil is excavated, and trenches are made for burying the e-waste in it. An impervious liner is made of clay or plastic with an effluent basin for collection and transferring the e-waste to the treatment plant. Landfilling is not an environmentally friendly method of e-waste disposal because it causes the release of toxic substances like mercury, cadmium, and lead into the soil and groundwater.
Acid Bath
In an acid bath, the electronic circuits are submerged in powerful and effective solutions of sulfuric, hydrochloric, or nitric acids that dissolve the metals from the electronic pathways. While the hazardous acid waste makes its way into the nearby water sources, the recovered metal is used in the production of other products.
Legal Status of E-Waste in India
There are laws in India to control how electronic waste is disposed of and managed. The following are the various laws that the Indian government has passed:
- The Hazardous Wastes (Management and Handling) Amendment Rules, 2003;
- Guidelines for Environmentally Sound Management of E-waste, 2008; and
- The E-waste (Management and Handling) Rules, 2011.
- E-Waste (Management) Second Amendment Rules, 2023
Latest amended rules related to E-waste
The E-Waste (Management) Second Amendment Rules, 2023, have been announced by the Central Government. On July 25, 2023, the regulations were released in the Official Gazette and are effective right away. The newly introduced provisions, which incorporate significant amendments to the current E-Waste (Management) Rules, 2022, emphasize the significance of using approved destruction such as cement kilns and plasma arc incinerators technologies for managing refrigerants. By concentrating on the refrigerants produced during the manufacture and end-of-life of refrigeration and air-conditioning equipment, these regulations seek to ensure secure, accountable, and sustainable management of e-waste. Guidelines are issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) to oversee the appropriate application of these technologies.
Methods for Managing E-Waste
- Online data storage
We don’t need to always carry a storage device with us because we can access our data by storing it online and accessing it from anywhere in the world. We can also get a lot of storage through cloud storage for free or at a very low cost. - Purchase energy-efficient electronics.
A device with a high Energy Star rating uses less energy, significantly lowering our electricity bill. Additionally, because less energy is needed, it prevents overuse, which controls resource (energy) depletion. - Raising awareness
To give those who depend on this for their livelihood better means, proper education, awareness, and, most importantly, alternative, cost-effective technology must be made available.
Challenges for e-waste disposal
India faces the following challenges in effective management of e-waste:
- Lack of infrastructure
The gap between e-waste that is being collected and recycled by authorized dismantlers/recyclers and the total quantum of e-waste being generated is huge. Issues with the current recycling facilities include a lack of environmentally sound technologies and a consistent supply of raw materials. This is primarily due to consumers selling their old electronics to unauthorized recyclers for quick cash because it is simpler and faster, and they are unaware of the hazardous effects of improper e-waste recycling. As a result, registered recycling facilities are cut off from a consistent flow of e-waste, which is essential to their survival. Currently, only a small portion of the total amount of generated e-waste is collected by India’s authorized e-waste recycling facilities; the remainder is recycled informally. - High cost of setting up recycling facilities
Advanced recycling technology is expensive and makes large investments risky, especially when sourcing e-waste is a challenge. Most of the formal recycling companies in India limit their role to only the pre-processing of e-waste, wherein the crushed e-waste with precious metals is exported to smelting refineries outside India. An end-to-end solution for e-waste recycling is still not available in India.
Growth of E-waste
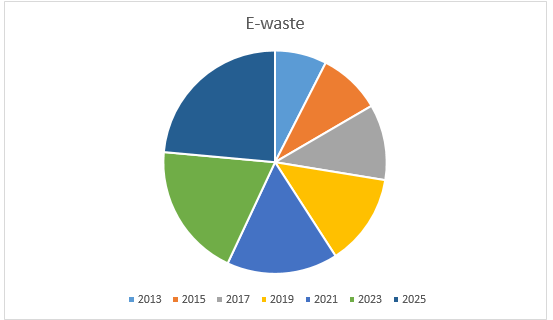
Source: Department of Information Technology
| YEAR | METRIC TON |
| 2013 | 589893 MT |
| 2015 | 713770 MT |
| 2017 | 863662 MT |
| 2019 | 1045031 MT |
| 2021 | 1264488 MT |
| 2023 | 1530030 MT |
| 2025 | 1851337 MT |
Enforcement Agencies related to e-waste disposal in India
- The Ministry of Environment and Forests of the Government of India is in charge of identifying hazardous wastes and granting permission to exporters and importers under the Environment (Protection) Act of 1986.
- Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), established under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act of 1974, together with the State Pollution Control Boards, coordinates activities and sees to it that import regulations are followed. Additionally, it conducts training sessions for authorities involved in the management of hazardous wastes, checks that the requirements for authorization, import, and export are being followed, and monitors compliance. It also suggests standards for treatment, disposal of waste, and material specifications, as well as guidelines for characterization of hazardous wastes. The CPCB has published SOPs and guidelines for processing e-waste. With the assistance of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, the CPCB and SPCBs have been monitoring the units and taking the necessary actions to mainstream and modernize the recycling industry.
- State Pollution Control Boards (SPCB) are organizations created under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act of 1974 with the mandate to identify and notify disposal sites, to grant and renew an authorization, to monitor compliance with the various provisions and conditions of an authorization, to forward importer applications, and to review other issues.
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade[1], established by the Foreign Trade (Development & Regulation) Act of 1992, has the power to grant or deny import permits for hazardous wastes under the Environment (Protection) Act of 1986.
- The Customs Act of 1962 requires port and customs authorities to verify documents, report any illegal traffic to the Ministry of Environment and Forests, analyze wastes that are allowed for import and export, and train officials in the handling of hazardous wastes and the rules governing them.
- The certification body for approving imports of used goods is the Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT).
Conclusion
To safeguard the environment and public health, it is imperative that e-waste management be addressed. We can ensure that hazardous materials are handled responsibly and valuable resources are recovered and reused by reducing, collecting, recycling, properly disposing of, and regulating e-waste. This will help us move towards a sustainable future.
FAQs
Electronic waste (e-waste) is a term used to describe all types of outdated, out-of-date, or discarded electrical and electronic equipment, including toys, leisure, sports, and recreational equipment that is powered by electricity, office computers, entertainment and consumer electronics, lighting equipment, and electrical and electronic tools. E-waste must be handled and recycled carefully because it contains valuable and hazardous materials.
Proper e-waste disposal is required because when e-waste is disposed of incorrectly, it can be hazardous. Heavy metals and toxic materials are used in the manufacture of electronic devices. Lead, cadmium, mercury, and other substances can leach into the soil and contaminate the air and waterways.
Some of the common methods for e-waste disposal are Landfilling, Acid Bath, Incineration, Recycling, Reuse
In addition to methane, landfills also release small amounts of oxygen, nitrogen, and other organic compounds that aren’t methane, as well as water vapor and carbon dioxide. Smog can be produced by these gases, and if they are not controlled, they can also contribute to climate change.
Reusing devices are by far the most environmentally friendly method of e-waste disposal. Many charities are happy to accept used electronics that can be repaired and given to those in less fortunate communities.
There are many beneficial uses for recycling e-waste. For instance, keeping those devices out of landfills would protect both human and environmental health. You could also retrieve the parts of the devices that are still functional and give manufacturers recycled metals to use in the creation of new products.
E-waste must be taken to a designated handler or recycler because they still contain hazardous materials even though they can be handled according to laxer standards.
Cadmium, mercury, lead, polybrominated flame retardants, barium, and lithium are just a few of the toxic materials found in electronic waste that are hazardous to human health. Humans exposed to these toxins can suffer damage to their brain, heart, liver, kidney, and skeletal systems.
Companies can manage E-waste responsibly and develop sustainability practices while saving money. Companies can manage e-waste in a variety of ways, including reducing pointless purchases, donating goods, collaborating with reliable recycling companies, and fixing electronics.
E-waste affects the groundwater table by leaching into the groundwater. As a result, it has an impact on drinking and domestic water because even small amounts of lead in water can pose health risks to both adults and children.
Both heavy metals and flame retardants can seep directly into the soil during improper e-waste disposal in regular landfills or in locations where it is illegally dumped. This can contaminate nearby or nearby crops, as well as the groundwater beneath them.
As more waste is sent to be burned, incinerators will release more toxins and pollutants that are bad for the local air quality. More harm is done to the local air quality by incinerating than by landfilling.
Read our Article:Popular E-Waste Disposal Methods In India













