Relevance of Waste Management Hierarchy in Business
 22 Sep, 2023
22 Sep, 2023 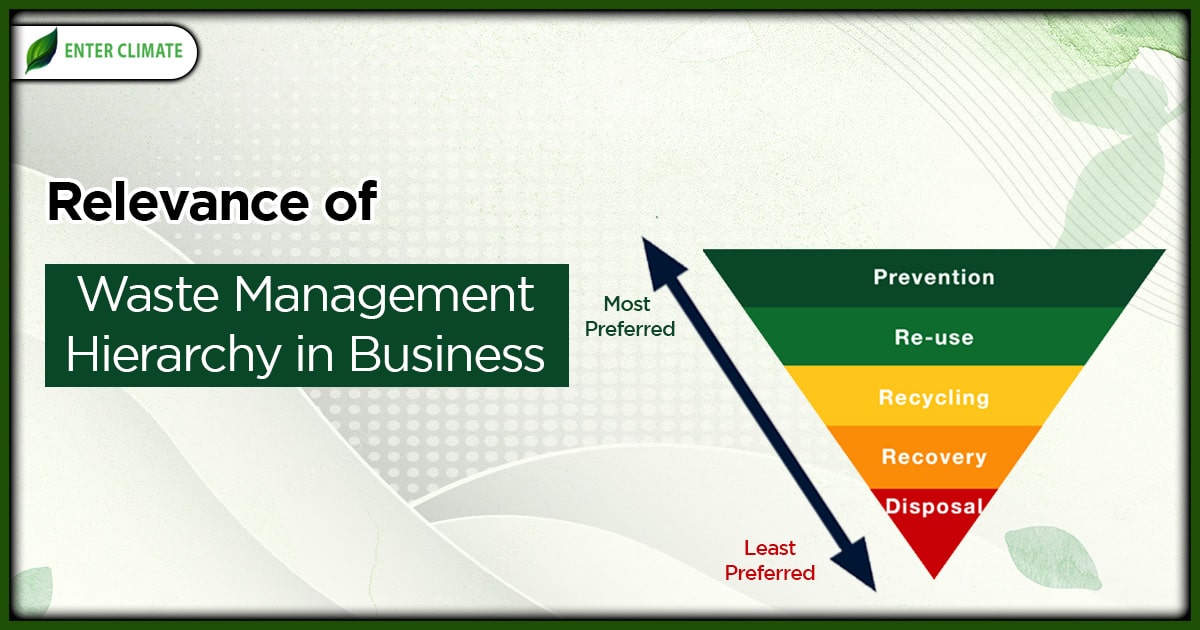
Most of the industry-related waste is hazardous, while some are non-hazardous. However, even if the waste is non-hazardous, it is essential to discard it properly. All kinds of waste business entities generate require management, recycling and proper disposal. In the past decade, waste management rules have become more elaborate and are governed by SOP for collection, transportation, recycling, reprocessing and disposal for stakeholders involved. Amid the growing concern over waste management in India, the source management of this waste has become crucial for Businesses. Proven Waste management hierarchy in industrial establishments is critical for the functioning of any business. As a business operator, one must strive to keep the organisation’s waste away from landfills and identify opportunities to manage waste better. Proper waste reduction strategies will make compliance easier and save the company moolah in the long run.
What does Waste Management Hierarchy mean?
The waste management hierarchy is a waste management framework designed to guide the decisions related to waste management at both the individual and organisational levels. It gives top priority to waste prevention. Such planning can help us restructure our relationship with waste based on five areas ranked in terms of what’s best for the business and the environment. This is often illustrated as an inverted pyramid model. This article will explain these five stages of the waste management hierarchy and how companies can design their strategy towards effective waste management.
This hierarchy can further assist the traditional waste management approach of “the three Rs,” i.e. reduce, reuse and recycle) by expanding it into a five-step process. i.e.
- Prevent
- Reduce
- Reuse
- Recycle
- Recover
The last stage is disposal, which includes landfilling the waste. The most preferred actions are at the top, and the least preferred at the bottom. The use of this hierarchy came with the emergence of life cycle thinking in the waste management policy. It looks at the product or service’s environmental impact, i.e. from raw material extraction to processing and manufacturing, and finally, distribution, usage and disposal.
Stages in Waste Management Hierarchy
By integrating such waste management, businesses and organisations can extract the most benefits, design better products and services, and minimise waste output. But what does each stage of the hierarchy mean? Let’s understand each of the stages of this waste management hierarchy.
REDUCE: The first stage of waste management focuses on minimising raw material usage, as this will lead to reducing or preventing as much waste generation as possible. Making reduction the top priority will help industries, communities and governments to reduce the use of virgin raw materials. The idea behind this approach is to prevent the unnecessary consumption of resources.
- Procuring raw materials with minimum packaging and requiring the fewest resources to refine.
- Avoiding the use of disposable or single-use goods.
- Procuring materials that are recycled or can be repaired or reused.
- Optimising inventory to prevent perishable goods from going to waste (e.g., food).
- If a business can’t reduce or prevent waste, one can also prepare them for reuse.
REUSE: Preparing materials for reuse is the second-best approach in the waste management hierarchy. Besides reducing your landfill impact, reusing business waste also allows businesses to avoid spending on virgin materials or paying a provider to dispose of their waste. For example, office-based firms can use these measures to prepare everyday items for reuse.
- Use durable glasses, cups, plates and cutlery instead of disposable or single-use items.
- Implementing a strategy to reuse packaging material like envelopes, boxes, etc. Selling used computers, furniture and other office equipment.
- Refilling toner and printer cartridges instead of purchasing new ones.
- A business can even generate income from waste that is valuable to other organisations.
Recycling involves processing used materials and turning them into new/ recycled products. It is the third step in the hierarchy because of the added energy and resources that go into creating a new product. To maximise recycling opportunities, a business must have the proper recycling infrastructure, including a waste management provider that can perform segregation, collection and recycling or an on-site recycling facility.
RECOVERY: When further recycling of the waste is not practical or possible, businesses can send the waste for energy or material recovery through processes such as:
- Incineration
- Gasification
- Anaerobic digestion
- Pyrolysis
DISPOSAL: When materials that cannot be reused, recycled or recovered for energy remain, the final approach that remains is landfilling. Landfilled and incinerated (without energy recovery) are a less desired method of waste management because the waste sitting in landfills can continue to have a damaging impact on the environment. Landfills can also leak toxic liquids and chemicals that can contaminate soil and groundwater underneath.
How to Implement a Waste Management Strategy in Business?
A waste management plan for a business can be done by following the 5-step waste management hierarchy. Here’s a breakdown of each step and how a business can implement it
Step 1: The first step is to focus on waste prevention. Identify areas in your business where waste can be minimised or eliminated. This can include reducing packaging, implementing efficient processes, and promoting responsible consumption.
Step 2: If waste prevention is not possible, the next step is waste minimisation. This involves finding ways to reduce the waste generated. Implement recycling programs, encourage employees to use resources efficiently, and explore opportunities for waste reduction in production processes.
Step 3: Encourage the reuse of materials whenever possible. Set up systems to collect and repurpose items such as packaging materials, office supplies, or equipment. Consider establishing partnerships with local organisations that can benefit from reusable materials.
Step 4: Establish a comprehensive recycling program within your business. Identify recyclable materials generated in your operations and set up collection systems. Educating employees about proper sorting and recycling practices and partnering with local recycling facilities or waste management companies will also help businesses ensure appropriate recycling and disposal of materials.
Step 5: The final step under the waste management hierarchy is responsible disposal. When waste cannot be prevented, minimised, reused, or recycled, it should be disposed of properly. Follow applicable waste disposal regulations and guidelines[1]. Businesses can also consider working with licensed waste management companies to ensure safe and environmentally sound disposal.
Conclusion
You must implement a proper waste management strategy to make a business sustainable. Implementing a waste management hierarchy requires commitment and engagement from employees at all levels. It’s essential to provide training and awareness programs, establish clear waste management policies, and regularly monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of your waste management practices. A business must remember that waste management is an ongoing process, and continuous improvement must be pursued. Regularly reviewing and updating one’s waste management strategy to adapt to changes in business operations and evolving best practices in the field will benefit businesses in the long run.
FAQs
The five R’s of waste management include reduce, reuse, recycle, recover and residual management.
Industrial waste is any substance rendered unusable during a production process, such as that of factories, mills, or mining activities. It is produced by industrial action and can include dirt, gravel, masonry, scrap metal, concrete, oil, solvents, chemicals, scrap lumber, and even vegetable waste from restaurants are examples of industrial waste.
Repurposing your industrial waste is an excellent way to reduce waste generation. For example, switch to items that can be refilled, like printer cartridges or glue, and reuse plastic folders. Use old wood and pallets to build compost bins. Reuse toiletries like shampoo bottles as cell charging stations and old toothbrushes as cleaning tools. Avoid paper towels, napkins, and tissues by going reusable.
Segregation of waste can reduce the waste burden on the already overflowing landfills. Businesses can segregate waste into two categories – Bio-Degradable and Non-Bio-Degradable. Putting wet scraps like leftover foods, vegetables, peels, etc., in an organic dustbin can later be used for composting, thereby curbing pollution levels.
Zero waste manufacturing, or ZWM, supports countries’ transition to a circular economy by using systems and technologies that eliminate waste across entire waste value chains to the fullest extent through reuse and recycling—implementation of ZWM.
The most straightforward answer to reducing waste in businesses is to go paperless. Companies can have emails and cloud-based systems to store their documents. Businesses can encourage employees and vendors to work with soft copies as much as possible.
Read our Article: Hazardous Waste Management













